Chemical Composition: Each 5 ml of solution contains: 3.335g Lactulose. Excipients: Sodium hydroxide, Banana flovour and purified water. Pharmacological Classifications: Gastrointestinal drugs (laxative).
Mechanism of action:
In the colon lactulose is broken down by colonic bacteria into low molecular organic acids. These acids lead to a lowering of pH in the colonic lumen and via an osmotic effect to an increase of the volume of colonic contents. These effects stimulate peristalsis of the colon and return the consistency of the stool. The constipation is cleared and the physiological rhythm of the colon is reinstated.
In hepatic encephalopathy (HE) the effect has been attributed to suppression of proteolytic bacteria by an increase of acidophilic bacteria (e.g. lactobacillus), trapping of ammonia in the ionic form by acidification of the colonic contents, catharsis due to the low pH in the colon as well as an osmotic effect, and alteration of the bacterial nitrogen metabolism by stimulating the bacteria to utilize ammonia for bacterial protein synthesis. Pharmacokinetics:
Lactulose is poorly absorbed after oral administration and it reaches the colon unchanged. There it is metabolised by the colonic bacterial flora. Metabolism is complete at doses up to 25 -50 g or 40-75 ml; at higher dosages, a proportion may be excreted unchanged.
Indications:
- For the treatment of constipation.
- For the treatment of hepatic encephalopathy (HE); hepatic coma
Contraindications:
Hypersensitivity to the active substance or any of the ingredients.
Galactosaemia.
Gastro-intestinal obstruction, digestive perforation or risk of digestive perforation
Side Effects:
Flatulence may occur during the first few days of treatment. As a rule it disappears after a couple of days.
- When dosages higher than instructed are used, abdominal pain and diarrhoea may occur.
Nausea and vomiting
Precautions:
Consultation of a physician is advised in case of:
Painful abdominal symptoms of undetermined cause before the treatment is started.
– Insufficient therapeutic effect after several days.
– Lactulose should be administered with care to patients who are intolerant to lactose.
The dose normally used in constipation should not pose a problem for diabetics.
The dose used in the treatment of HE is usually much higher and may need to be taken into consideration for diabetics.
Chronic use of unadjusted doses and misuse can lead to diarrhoea and disturbance of the electrolyte balance. This product contains lactose, galactose and small amounts of fructose, Patients with rare hereditary problems of galactose intolerance, the Lapp lactase deficiency or glucose-galactose malabsorption should not take this medicine. – Use of laxatives in children should be exceptional and under medical supervision.
Pregnancy: No effects during pregnancy are anticipated, since systemic exposure to lactulose is negligible. Lactulose can be used during pregnancy.
Lactation: Lactulose can be used during breast-feeding.
Drug and Food Interactions: None known.
Dosage and Method of Administration:
The lactulose solution may be administered diluted or undiluted. Each dose may if necessary be taken with water or fruit juices, etc.
Each dose of lactulose should be swallowed in one and should not be kept in the mouth for an extended period of time. The posology should be adjusted according to the individual needs of the patient.
In case of single daily dose, this should be taken at the same time, e.g. during breakfast.
During the therapy with laxatives it is recommended to drink sufficient amounts of fluids (1.5-2 litres, equal to 6-8 glasses) during the day.
Dosing in constipation: Lactulose may be given as a single daily dose or in two divided doses, the measuring cup may be used. After a few days the starting dosage may be adjusted to the maintenance dose based upon treatment response. Several days (2-3 days) of treatment may be needed before treatment effect occurs.
Maintenance daily dose
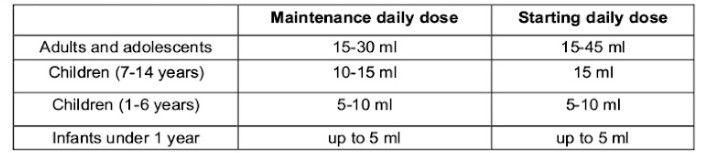
Dosing in HE (for adults only): Starting dose: 3 to 4 times daily 30 -45 ml (6-9 x 5 ml spoonfuls). This dose may be adjusted to the maintenance dose to achieve two or three soft stools each day.
Overdosage:
Symptom: diarrhoea and abdominal pain.
Treatment: cessation of treatment or dose reduction. Extensive fluid loss by diarrhoea or vomiting may require correction of electrolyte disturbances.
No specific antidote. Symptomatic treatment should be given.
Storage Conditions:Store at room temperature 15-30 °C.Keep out of reach of children. Don’t freeze.
Packaging: Glass bottle of 100ml Lactulose/carton box, with measured plastic cup.