The use of ACE inhibitors is contra-indicated during the 2nd and 3rd trimester of pregnancy.
Composition:Each tablet contains perindopril Erbumine 2 or 4 or 8 mg
- The use of ACE inhibitors is not recommended during the first trimester of pregnancy.
Warning:
Pharmacokinetics:
Excipients: Microcrystalline cellouse, Anhydrous lactouse, Magnesium Stearate, Silicone dioxide. Mechanism of action
perindopril is an inhibitor of the enzyme that converts angiotensin I into angiotensin II .It is possible that this mechanism contributes to the blood pressure-lowering action of ACE inhibitors.
- After oral administration, the absorption of perindopril is rapid .The plasma half-life of perindopril is equal to 1 hour Perindopril is a prodrug .Twenty seven percent of the administreted perindopril dose reaches the blood stream as the active metabolite
- perindoprilat .In addition to active perindoprilat, perindopril yields five metabolites, all inactive. The peak plasma concentration of perindoprilat is achieved within 3 to 4 hours.
- As ingestion of food decreases conversion to perindoprilat, hence bioavailability, perindopril should be administered orally in a single daily dose in the morning before a meal. Protein binding of perindoprilat to plasma proteins is 20%.
- Perindoprilat is eliminated in the urine and the half-life of the unbound fraction is approximately 17 hours resulting in steady-state within 4 days.
Indications:
- Hypertension.
- Heart failure(Only for 2,4 mg strengths).
- Stable coronary artery disease.
Contraindications:
- Hypersensitivity to perindopril, to any of the excipients.
- History of angioedema associated with previous ACEI therapy.
- Hereditary of idiopathic angioedema.
- Second and third trimesters of pregnancy.
The concomitant use of Perindopril tert-butylamine with aliskiren- containing products is contraindicated in patients with diabetes mellitus or renal impairment (GFR< 60 ml/min/1.73 m2). Pregnancy and lactation:
The use of ACE inhibitors is not recommended during the first trimester of pregnancy .The use of ACE inhibitors is contraindicated during the second and third trimester of pregnancy.
Because no information is available regarding the use of Perindopril during breastfeeding, Perindopril is not recommended during breast-feeding. Adverse effect:
The common side effects are:
Headache, dizziness, vertigo, paresthaesia, tinnitus,vision disturbance, hypotension and effects related to hypotension, cough, dyspnea, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, dyspepsia, diarrhea, constipation, rash, pruritus, muscle cramps and asthenia. The uncommon side effects are: mood or sleep disturbances, bronchospasm, dry mouth, angioedema, urticaria, renal insufficiency, impotence, sweating. Warning:
Stable coronary artery disease:
If an episode of unstable angina pectoris (major or not) occurs during the first month of perindopril treatment, a careful appraisal of the benefit/risk should be performed before treatment continuation. Hypotension :
ACE inhibitors may cause a fall in blood pressure. Symptomatic hypotension is seen rarely in uncomplicated hypertensive patients and is more likely to occur in patients who have been volume-depleted. If hypotension occurs, the patient should be placed in the supine position and, if necessary, should receive an intravenous infusion of normal saline .A transient hypotensive response is not a contraindication to further doses. In some patients with congestive heart failure who have normal or low blood pressure, additional lowering of systemic blood pressure may occur with perindopril .If hypotension becomes symptomatic, a reduction of dose or discontinuation of perindopril may be necessary.
Aortic and mitral valve stenosis / hypertrophic cardiomyopathy:
As with other ACE inhibitors, perindopril should be given with caution to patients with mitral valve stenosis and
obstruction in the outflow of the left ventricle such as aortic stenosis or hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Renal impairment:
In cases of renal impairment (creatinine clearance < 60 ml/min) the initial perindopril dosage should be adjusted according to the patient’s creatinine clearance.
In patients with symptomatic heart failure, hypotension following the initiation of therapy with ACE inhibitors may lead to some further impairment in renal function. Acute renal failure, usually reversible, has been reported in this situation.
In some patients with bilateral renal artery stenosis or stenosis of the artery to a solitary kidney, who have been treated with ACE inhibitors, increases in blood urea and serum creatinine, usually reversible upon discontinuation of therapy have been seen.
Some hypertensive patients with no apparent pre-existing renal vascular disease have developed increases in blood urea and serum creatinine, usually minor and transient, especially when perindopril has been given concomitantly with a diuretic. This is more likely to occur in patients with pre-existing renal impairment. Dosage reduction and/or discontinuation of the diuretic and/or perindopril may be required. Haemodialysis patients:
Anaphylactoid reactions have been reported in patients dialysed with high flux membranes, and treated concomitantly with an ACE inhibitor. Hypersensitivity/Angioedema :
Angioedema of the face, extremities, lips, mucous membranes, tongue, glottis and/or larynx has been reported rarely in patients treated with ACE inhibitors, including Perindopril. Angioedema associated with laryngeal oedema may be fatal,the condition generally resolved without treatment, although antihistamines have been useful in relieving symptoms .Intestinal angioedema has been reported rarely in patients treated with ACE inhibitors, These patients presented with abdominal pain (with or without nausea or vomiting). Patients with a history of angioedema unrelated to ACE inhibitor therapy maybe at increased risk of angioedema while receiving an ACE inhibitor.
Anaphylactoid reactions during desensitisation:
There have been isolated reports of patients experiencing sustained, life-threatening anaphylactoid reactions while receiving ACE inhibitors during desensitization treatment with hymenoptera (bees, wasps) venom.
Hepatic failure : Patients receiving ACE inhibitors who develop jaundice or marked elevations of hepatic enzymes should discontinue the ACE inhibitor and receive appropriate medical follow-up.
Neutropenia/Agranulocytosis/Thrombocytopenia/Anemia have been reported in patients receiving ACE inhibitors .Perindopril should be used with extreme caution in patients with collagen vascular disease, immunosuppressant therapy, treatment with allopurinol or procainamide, or a combination of these complicating factors, especially if there is pre-existing impaired renal function.
Cough Cough has been reported with the use of ACE inhibitors,the cough is non-productive, persistent and resolves after discontinuation of therapy. Surgery/Anesthesia: The treatment should be discontinued one day prior to the surgery.
Hyperkalaemia:
Elevations in serum potassium have been observed in some patients treated with ACE inhibitors, Hyperkalemia can cause serious, sometimes fatal arrhythmias. If concomitant use of agents that increase serum potassium is deemed appropriate, they should be used with caution and with frequent monitoring of serum potassium.
Diabetic patients:
In diabetic patients treated with oral antidiabetic agents or insulin, glycaemic control should be closely monitored during the first month of treatment with an ACE inhibitor.
Lithium:The combination of lithium and perindopril is generally not recommended.
Potassium sparing diuretics, potassium supplements or potassium containing salt substitutes:
The combination of perindopril and potassium sparing diuretics, potassium supplements or potassium containing salt substitutes is generally not recommended. Pregnancy:
ACE inhibitors should not be initiated during pregnancy. When pregnancy is diagnosed, treatment with ACE inhibitors should be stopped immediately, and if appropriate, alternative therapy should be started.
Dual blockade of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS):
There is evidence that the concomitant use of ACE-inhibitors, angiotensin II receptor blockers or aliskiren increases the risk of hypotension, hyperkalaemia and decreased renal function (including acute renal failure).
Drug interactions:
- Diuretics:Patients on diuretics, and especially those who are volume and/or salt depleted, may experience excessive reduction in blood pressure after initiation of therapy with an ACE inhibitor.
- Potassium sparing diuretics, potassium supplements or potassium-containing salt substitutes :Although serum potassium usually remains within normal limits, the combination of perindopril with the above-mentioned drugs is not recommended.
Lithium:Reversible increases in serum lithium concentrations and toxicity have been reported during concomitant administration of lithium with ACE inhibitors. Use of perindopril with lithium is not recommended.
(Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs) NSAIDs (including aspirin≤ 3 g/day:When ACE-inhibitors are administered simultaneously with non-steroidal anti- inflammatory drugs, attenuation of the antihypertensive effect may occur.
Anti hypertensive agents and vasodilators: Concomitant use of these agents may increase the hypotensive effects of perindopril.
- Antidiabetic agents:concomitant administration of ACE inhibitors and antidiabetic medicines (insulin,oral hypoglycemic agents) may cause an increased blood- glucose lowering effect. This phenomenon appeared to be more likely to occur during the first weeks of combined treatment and in patients with renal impairment.
- Tricyclicantidepressants/Antipsychotics/Anesthetics:Concomitant use of certain anesthetic medicinal products, tricyclic antidepressants and antipsychotics with ACE inhibitors may result in further reduction of blood pressure.
- Sympathomimetics: Sympathomimetics may reduce the antihypertensive effects of ACE inhibitors.
- Gold: Nitritoid reactions (symptoms include facial flushing, nausea, vomiting and hypotension) have been reported rarely in patients on therapy with injectable gold (sodium aurothiomalate) and concomitant ACE inhibitor therapy including perindopril.
Dosage and administration:
It is recommended that Perindopril tert-butyl amine is taken once daily in the morning before a meal with sufficient amount of fluid. Hypertension:
Perindopril tert butyl amine may be used in monotherapy or in combination with other classes of antihypertensive therapy .The recommended starting dose is 4 mg given once daily in the morning. Patients with a strongly activated renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system may experience an excessive drop in blood pressure following the initial dose. A starting dose of 2 mg is recommended in such patients and the initiation of treatment should take place under medical supervision. The dose maybe increased to 8 mg once daily after one month of treatment .Symptomatic hypotension may occur following initiation of therapy with perindopril; this is more likely in patients who are being treated concurrently with diuretics. Caution is therefore recommended since these patients may be volume and/or salt depleted. If possible, the diuretic should be discontinued 2 to 3 days before beginning therapy with perindopril. In hypertensive patients in whom the diuretic cannot be discontinued, therapy with perindopril should be initiated with a 2 mg dose. In elderly patients treatment should be initiated at a dose of 2 mg which may be progressively increased to 4 mg after one month then to 8 mg if necessary depending on renal function. Symptomatic heart failure(Only for 2,4 mg strengths):
It is recommended that Perindopriltert-butylamine, generally associated with non potassium-sparing diuretic and/or digoxin and/or a beta blocker, be introduced under close medical supervision with a recommended starting dose of 2 mg taken in the morning. This dose maybe increased by increments of 2 mg at intervals of no less than 2 weeks to 4 mg once daily if tolerated.
Stable coronary artery disease:
Perindopriltert-butylamine should be introduced at a dose of 4 mg once daily for two weeks, then increased to 8 mg once daily. depending on renal function and provided that 4 mg dose is well tolerated.
Elderly patients should receive 2 mg once daily for one week, then 4 mg once daily the next week, before increasing the dose up to 8 mg once daily depending on renal function.
Dosage adjustment in renal impairment:
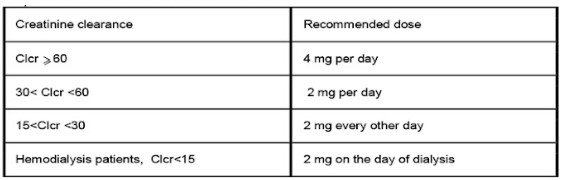
Dosage in patients with renal impairment should be based on creatinine clearance.
Creatinine clearance
Dosage adjustment in hepatic impairment:
No dosage adjustment is necessary in patients with hepatic impairment.
Children and adolescents:
Efficacy and safety use in children has not been established .Therefore, use in children is not recommended. Overdosage:
Symptoms associated with overdose of ACE inhibitors may include hypotension, circulatory shock, electrolyte disturbances, renal failure hyperventilation, tachycardia, palpitations, bradycardia, dizziness, anxiety, and cough .The recommended treatment of overdose is intravenous infusion of normal saline solution .If hypotension occurs, the patient should be placed in the shock position .If available, treatment with angiotensinll infusion and/or intravenous catecholamines may also be considered .Perindopril may be removed from the general circulation by haemodialysis:
Storage condition”: Store at room temperature (15-25)°C, away from moisture”.
Packaging: 2or 3 blister, each contains 10 tablets/carton box.