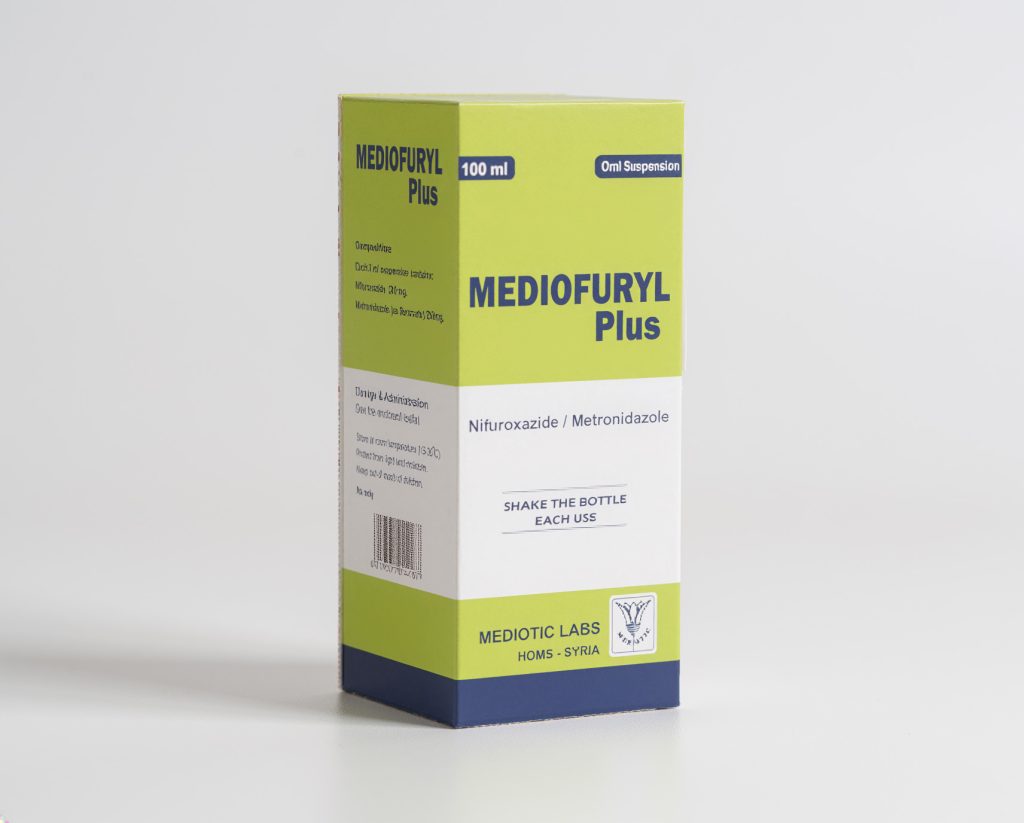
Nifuroxazide+ Metronidazole
200/250mg in 5 ml suspension
Chemical composition: Each 5 ml suspension contains: NIFUROXAZIDE
200 mg + METRONIDAZOLE (as benzoate) 250 mg.
Excipients: Cellulose, Sugar, Banana flavor, Glycerin, Polysorbate 80, Sorbitol, Methyl paraben, Propyl paraben. PHARMACOKINETICS AND
PHARMACODYNAMICS:
The presence of nifuroxazide is given in order to achieve a drug synergy avoiding amoeba-bacteria symbiosis. Nifuroxazide is an intestinal antiseptic with strictly local antibacterial action. Nifuroxazide has the advantage of not affecting the intestinal saprophytic flora. It is effective against Escherichia coli, S. paratyphi, S. faecalis and S. dysenteriae, so indicated for cases of bacillary dysentery and infectious diarrhea. Pseudomonas is resistant nature.
It is not absorbed through the digestive tract unless there is a significant lesion at the mucosal level. The treatment with this combination should not be extended to more than ten days because of the medical indication previously proposed. Due to the formulation presented, fewer doses are needed to administer metronidazole. Nitrofurans inhibit the synthesis of ATP by blocking the enzymatic systems at the level of the bacterial Krebs cycle.
Metronidazole is a synthetic oral antiparasitic, which is well absorbed orally. Its half-life is 8 hours with fecal excretion of 6 to 15% of the administered dose.
It is also known for its antibacterial properties. Its biotransformation is carried out by oxidation, reduction and conjugation with glucuronic acid. Renal clearance is approximately 10 ml/min.
The plasma protein binding of the circulating metronidazole is approximately 20%. The presence of food does not affect the absorption of metronidazole metronidazole are effective against Entamoeba histolytica, Trichomonas vaginalis and Giardia lamblia (at concentrations of 1 to 50 mcg/mL in vitro). Its mechanism of action is inhibitor of the DNA synthesis of the parasite or the bacteria affected.
The original metronidazole and some of its metabolites are excreted in various proportions in the urine, after the subject ingests the primary compound. The liver is the main organ in which it is metabolized.
INDICATIONS:
Extraintestinal and luminal amebiasis associated with bacterial intestinal infection. Intestinal Giardiasis, associated with bacterial intestinal infection.
CONTRAINDICATIONS:
Patients with a history of nitrofuran allergy and hypersensitivity to metronidazole.
First trimester of pregnancy.
PRECAUTIONS:
Patients with severe hepatic disease metabolize metronidazole slowly resulting accumulation of this and its metabolites in plasma. Therefore, low doses with close monitoring are recommended for such patients. Candidiasis symptoms may be exacerbated during metronidazole therapy, requiring treatment with an anticandiditic agent.
Seizures and peripheral neuropathy have been reported in patients treated with metronidazole, the presence of abnormal neurological signs requires prompt discontinuation of metronidazole therapy. Metronidazole should be administered with caution to patients with central nervous system disease.
Prolonged administration of the product may interfere with the results of normal transaminase, lactate dehydrogenase and triglyceride values.
Patients with impaired hepatic function may modify the plasma clearance of metronidazole.
PREGNANCY AND BREASTFEEDING:
The product should not be used in pregnant women if the benefit / risk index is not justified primarily during the first quarter. Do not use in lactating or children under 2 years.
MUTAGENESIS AND FERTILITY:
In experimental studies it has been observed that metronidazole has a potential for carcinogenesis in both rats and mice. At the same time, in a large number of biological in vitro assays metronidazole has shown mutagenic activity.
There are currently no controlled studies with the product in pregnant women.
ADVERSE REACTIONS:
There may be nausea 12%, headache, anorexia, metallic taste, glossitis, among others.
CNS: Dizziness, ataxia, confusion, insomnia, irritability and in some cases the presence of seizures and peripheral neuropathy. In cardiovascular system: ECG monitoring The flattening of the T wave.
Drugs interactions:
Intolerance may occur with sucrose.
Increased hypoprothrombinemic response of warfarin, and bleeding occur in some patients receiving both drugs simultaneously. With phenobarbital the medication can cause a decrease in the concentration of blood metronidazole, by increasing the metabolism of the latter.
With cimetidine on the other hand it can increase the blood concentration of metronidazole.
Metronidazole and simultaneous disulfiram may produce CNS toxicity, probably by the inhibition of aldehyde dehydrogenase. Administration of etronidazole with the presence of ethyl alcohol may trigger a reaction similar to that of disulfiram used in addicted individuals.
With phenytoin, metronidazole may cause an increase in the plasma concentration of phenytoin.
Dosage and method of administration:
Administration way: Oral.
Suspension(children above 2 years old): The recommended dose is 3 to 4 teaspoons per day in 3 divided doses. OVERDOSAGE:
Symptoms that refer to the presence of an overdose are: Nausea, vomiting, ataxia mainly due to the appearance of metronidazole. No specific antidote is known. Administration of 15 g of total metronidazole as a suicide attempt has been reported. The management of the patient in cases of overdose consists of the application of a supportive and symptomatic treatment quickly.
Storage conditon: “store at room temperature, 15°-30°C, away from light”
Packaging: Glass bottle of 100 ml/carton box with Measuring plastic Cup.
THIS IS A MEDICAMENT *
“Keep out of reach of children”.