Oseltamivir 30, 45, 75 mg
Composition: Each capsule contains: 30 mg, 45 mg, or 75 mg oseltamivir, in the form of oseltamivir phosphate. Excipients: pregelatinized starch, talc, povidone, croscarmellose sodium, and magnesium stearate. Mechanism Of Action:
Oseltamivir is an antiviral drug with activity against influenza virus.
Pharmacokinetics:
Absorption and Bioavailability: Oseltamivir is absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract after oral administration of oseltamivir phosphate and is extensively converted predominantly by hepatic esterases to oseltamivir carboxylate. At least 75% of an oral dose reaches the systemic circulation as oseltamivir carboxylate and less than 5% of the oral dose reaches the systemic circulation as oseltamivir.
Coadministration with food had no significant effect on the peak plasma concentration, and the area under the plasma concentration time curve of oseltamivir carboxylate.
Distribution: The volume of distribution (Vss) of oseltamivir carboxylate, following intravenous administration in 24 subjects, ranged between 23 and 26 liters. The binding of oseltamivir carboxylate to human plasma protein is low (3%). The binding of oseltamivir to human plasma protein is 42%, which is insufficient to cause significant displacement-based drug interactions.
Elimination: Absorbed oseltamivir is primarily (>90%) eliminated by conversion to the active metabolite, oseltamivir carboxylate. Plasma concentrations of oseltamivir declined with a half-life of 1 to 3 hours in most subjects after oral administration. Oseltamivir carboxylate is not further metabolized and is eliminated unchanged in urine. Plasma concentrations of oseltamivir carboxylate declined with a half-life of 6 to 10 hours in most subjects after oral administration.
Metabolism: Oseltamivir is extensively converted to the active metabolite, oseltamivir nor oseltamivir carboxylate is a substrate for, or inhibitor of, cytochrome P450 isoforms.
Excretion: Oseltamivir carboxylate is eliminated entirely (>99%) by renal excretion. Less than 20% of an oral radiolabeled dose is eliminated in feces.
Indications:
it is indicated for:
– Treatment of acute, uncomplicated influenza A and B in patients 2 weeks of age and older who have been symptomatic for no more than 48 hours.
– Prophylaxis of influenza A and B in patients 1 year and older.
Limitations of Use:
– Not a substitute for annual influenza vaccination.
– Consider available information on influenza drug susceptibility patterns and treatment effects when deciding whether to use.
Not recommended for patients with end-stage renal disease not undergoing dialysis.
Contraindications:
it is contraindicated in patients with known serious hypersensitivity to oseltamivir or any component of the product. Severe allergic reactions have included anaphylaxis and serious skin reactions including toxic epidermal necrolysis, Stevens-Johnson Syndrome, and erythema multiforme .
Side Effects:
Most common adverse reactions include:
Nausea, vomiting, headache. The common adverse reactions is Bronchitis, Herpes, Nasopharyngitis, Upper respiratory tract infections, Sinusitis, Insomnia, Cough, Sore throat, Rhinorrhea, Abdominal pain (incl. upper abdominal pain), Dyspepsia, Pain, Dizziness (incl. vertigo), Fatigue, Pyrexia, Pain in limb (Treatment studies). Cough, Nasal congestion, vomiting, headache, Otitis media, Conjunctivitis(including red eyes, eye discharge and eye pain), Earache, Rhinorrhoea, Abdominal pain (incl. upper abdominal pain), Dyspepsia, Nausea (Prophylaxis studies). Paediatric population (infants less than one year of age): vomiting, diarrohea and diaper rash being the most frequently reported adverse events.
Precautions & Warnings:
Serious Skin/Hypersensitivity Reactions: Cases of anaphylaxis and serious skin reactions including toxic epidermal necrolysis, Stevens-Johnson Syndrome, and erythema multiforme have been reported in postmarketing experience. Stop THE DRUG and institute appropriate treatment if an allergic-like reaction occurs or is suspected. Neuropsychiatric Events: There have been postmarketing reports of delirium and abnormal behavior leading to injury, and in some cases resulting in fatal outcomes, in patients with influenza who were receiving the drug. These events were reported primarily among pediatric patients and often had an abrupt onset and rapid resolution. Influenza can be associated with a variety of neurologic and behavioral symptoms that can include events such as hallucinations, delirium, and abnormal behavior, in some cases resulting in fatal outcomes. These events may occur in the setting of encephalitis or encephalopathy but can occur without obvious severe disease. Closely monitor the drug-treated patients with influenza for signs of abnormal behavior. If neuropsychiatric symptoms occur, evaluate the risks and benefits of continuing THE DRUG for each patient.
Risk of Bacterial Infections: There is no evidence for efficacy of the drug in any illness caused by pathogens other than influenza viruses. Serious bacterial infections may begin with influenza-like symptoms or may coexist with or occur as complications during the course of influenza. Oseltamivir has not been shown to prevent such complications. Prescribers should be alert to the potential for secondary bacterial infections and treat them as appropriate.
Fructose Intolerance In Patients With Hereditary Fructose Intolerance
Fructose can be harmful to patients with hereditary fructose intolerance. One dose of 75 mg THE DRUG for oral suspension delivers 2 grams of sorbitol. This is above the daily maximum limit of sorbitol for patients with hereditary fructose intolerance, and may cause dyspepsia and diarrhea.
Drug Interactions:
Influenza Vaccines:
Live Attenuated Influenza Vaccine :
The concurrent use of Oseltamivir with live attenuated influenza vaccine (LAIV) intranasal has not been evaluated. However, because of the potential for Oseltamivir to inhibit replication of live vaccine virus and possibly reduce the efficacy of LAIV, avoid administration of LAIV within 2 weeks before or 48 hours after Oseltamivir administration, unless medically indicated.
Inactivated Influenza Vaccine :
Inactivated influenza vaccine can be administered at any time relative to use of oseltamivir.
Pregnancy: Pregnancy Category C
Oseltamivir should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus. Nursing Mothers:
Based on limited published data, Oseltamivir and oseltamivir carboxylate are present in human milk at low levels considered unlikely to lead to toxicity in the breastfed infant. Exercise caution when Oseltamivir is administered to a nursing woman.
Renal Impairment: Patients with renal impairment had higher blood levels of oseltamivir carboxylate compared to patients with normal renal function which may increase the risk of Oseltamivir -associated adverse reactions. Therefore, dosage adjustment is recommended for patients with a serum creatinine clearance between 10 and 60 mL/minute and for patients with end-stage renal disease (ESRD) undergoing routine hemodialysis or continuous peritoneal dialysis treatment. Oseltamivir is not recommended for patients with ESRD not undergoing dialysis.
Hepatic Impairment:
No dosage adjustment is required in patients with mild to moderate hepatic impairment. The safety and
pharmacokinetics in patients with severe hepatic impairment have not been evaluated.
Use in Patients with Chronic Conditions: Efficacy of Oseltamivir in the treatment of influenza in patients with chronic cardiac disease and/or respiratory disease was evaluated in one randomized, placebo-controlled clinical trial. Efficacy in this population, as measured by time to alleviation of all symptoms, was not established, but no new safety signals were identified.
Immunocompromised Patients:
Efficacy of Oseltamivir for the treatment or prophylaxis of influenza has not been established in immunocompromised patients. Safety of Oseltamivir for prophylaxis of influenza has been demonstrated for up to 12 weeks in
immunocompromised patients.
Dosage & Administration:
The capsules and oral suspension may be taken with or without food; however, tolerability may be enhanced if it is taken with food
Treatment of influenza:
Adults and adolescents (13 years and older): 75 mg twice daily for 5 days (one 75 mg capsule or 12.5 mL of oral suspension twice daily) for 5 days.
for oral suspension (supplied as a powder,capsules may be opened and mixed with sweetened liquids such as regular or sugar-free chocolate syrup, corn syrup, caramel topping, or light brown sugar (dissolved in water). This is the preferred formulation (6 mg per mL) for patients who cannot swallow capsules.
Therapy should be initiated as soon as possible within the first two days of onset of symptoms of influenza. Post-exposure prevention: The recommended dose for prevention of influenza following close contact with an infected individual is 75 mg oseltamivir once daily for 10 days for adolescents (13 to 17 years of age) and adults.
Body Weight Recommended dose for 5 days 40 kg< 75 mg twice daily Body Weight Recommended dose for 10 days 40<kg 75 mg once daily
Therapy should begin as soon as possible within two days of exposure to an infected individual.
Prevention during an influenza epidemic in the community: The recommended dose for prevention of influenza during a community outbreak is 75 mg oseltamivir once daily for up to 6 weeks.
Paediatric population
Children 1 to 12 years of age
30 mg, 45 mg and 75 mg capsules and oral suspension are available for infants and children 1 year of age or older Treatment: The following weight-adjusted dosing regimens are recommended for treatment of infants and children 1 year of age or older:

Prevention during an influenza epidemic in the community: The recommended dose for prevention of influenza during a community outbreak is 75 mg oseltamivir once daily for up to 6 weeks.
Paediatric population
Children 1 to 12 years of age
30 mg, 45 mg and 75 mg capsules and oral suspension are available for infants and children 1 year of age or older Treatment: The following weight-adjusted dosing regimens are recommended for treatment of infants and children 1 year of age or older:
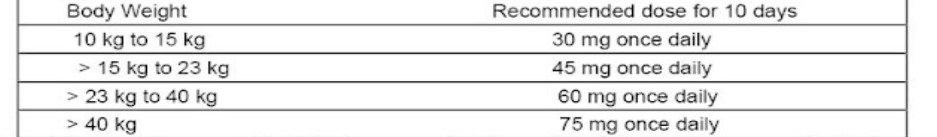
Treatment should be initiated as soon as possible within the first two days of onset of symptoms of influenza. Post-exposure prevention: The recommended post-exposure prevention dose of is:
Body Weight
10 kg to 15 kg
> 15 kg to 23 kg
> 23 kg to 40 kg
> 40 kg
Recommended dose for 10 days
30 mg once daily
45 mg once daily
60 mg once daily
75 mg once daily
Prevention during an influenza epidemic in the community: Prevention during an influenza epidemic has not been studied in children below 12 years of age. Infants 0
–
12 months of age
Treatment: The recommended treatment dose for infants 0 – 12 months of age is 3 mg/kg twice daily. The following dosing regimen is recommended for treatment of infants 0 – 12 months of age:
Body weight
3 kg
Recommended dose for 5 days
9 mg twice daily
12 mg twice daily
4 kg
5 kg
6 kg
15 mg twice daily
18 mg twice daily
9 kg 10 kg
27 mg twice daily
30 mg twice daily
One large oral dose dispenser to measure out water – a 5 or 10 ml dispenser
One small oral dose dispenser showing measurements of 0.1 ml, to give the dose Teaspoon (5 ml spoon)
Water
Sweet food to hide the bitter taste of the powder
Examples are: chocolate or cherry syrup and dessert toppings such as caramel or fudge sauce.
Or you can make sugar water: mix a teaspoon of water with three-quarters (3/4) of a
teaspoon of sugar.
Step 1: Pour all the powder into a bowl
Hold a 75 mg capsule upright over one of the bowls and carefully snip off the rounded tip with scissors. Be careful with the powder: it may irritate your skin and eyes.
Pour all of the powder into the bowl, whatever the dose you are making.
The amount is the same whether you are treating or preventing flu.
Repeat this procedure every time you need to give the medicine.
Step 2: Add water to dilute the medicine
Use the larger dispenser to draw up 12.5 ml water. Add the water to the powder in the bowl. Stir the mixture with the teaspoon for about 2 minutes.
Don’t worry if not all of the powder dissolves. The undissolved powder is just inactive ingredients.
Step 3: Choose the correct amount for your child’s weight
Look up the child’s weight on the left side of the table.
The column on the right of the table shows how much of the liquid mixture you will need to draw up. Infants less than 1 year (including full-term newborn babies)
Child’s weight(nearest)
3 kg 3.5 kg
How mixture to draw much up
1.5 ml
1.8 ml
2.0 ml
4 kg
2.3 ml
4.5 kg
2.5 ml
5 kg
2.8 ml
5.5 kg
3.0 ml
6 kg
3.3 ml
6.5 kg
3.5 ml
7 kg
3.8 ml
7.5 kg
4.0 ml
8 kg
4.3 ml
8.5 kg
4.5 ml
9 kg
4.8 ml
9.5 kg
10 kg or more
Children 1 year or older, weighing less than 40 kg
Child’s weight (nearest)
5.0 ml
How much mixture to draw up
5.0 ml
Up to 15 kg
15 to 23 kg
7.5 ml
10.0 ml
23 to 40 kg
Step 4: Draw up the liquid mixture
Make sure you have the right size dispenser.
Draw up the correct amount of liquid mixture from the first bowl.
Draw it up carefully so as not to include air bubbles.
Gently squirt the correct dose into the second bowl.
Step 5: Sweeten and give to the child
Add a small amount – no more than one teaspoonful – of a sweet food to the second bowl.
This is to hide the bitter taste of the powder.
Mix the sweet food and the liquid well.
Give the whole contents of the second bowl (liquid mixture with sweet food added) to the child straight away.
If there is anything left in the second bowl, rinse the bowl with a small amount of water and get the child to drink it all. For children unable to drink from a bowl, spoon-feed or use a bottle to feed the child the remaining liquid.
Give the child something to drink.
Throw away any unused liquid left in the first bowl.
Repeat this procedure every time you need to give the medicine
Data derived from studies in continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis (CAPD) patients; the clearance of oseltamivir carboxylate is expected to be higher when automated peritoneal dialysis (APD) mode is used. Treatment mode can be switched from APD to CAPD if considered necessary by a nephrologist.
There is insufficient clinical data available in infants and children (12 years of age and younger) with renal impairment to be able to make any dosing recommendation.
Elderly:
No dose adjustment is required, unless there is evidence of moderate or severe renal impairment. Immunocompromised patients:
Treatment: The recommended oral dose is 75 mg oseltamivir twice daily for 10 days for adults .Treatment should be initiated as soon as possible within the first two days of onset of symptoms of influenza.
Seasonal prophylaxis: Longer duration of seasonal prophylaxis up to 12 weeks has been evaluated in
immunocompromised patients
Overdosage:
In the majority of cases reporting overdose, no adverse reactions were reported. Adverse reactions reported following overdose were similar in nature to those observed with therapeutic doses of Oseltamivir.
Packaging: TAMIMED (30,45.75) 1 blister contains 10 capsules/carton box.
Storage Conditions: “Store at room temperature, 15° – 30° C”,
“Keep out of reach of children